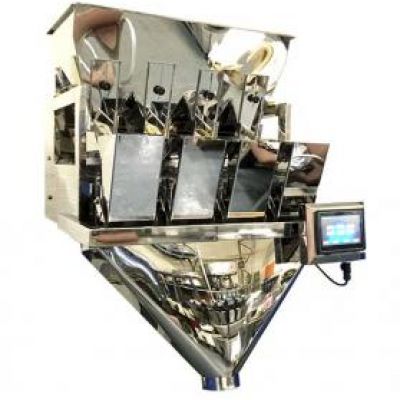
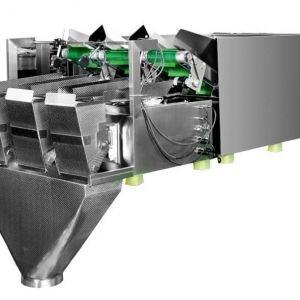
What is a Linear Weigher?
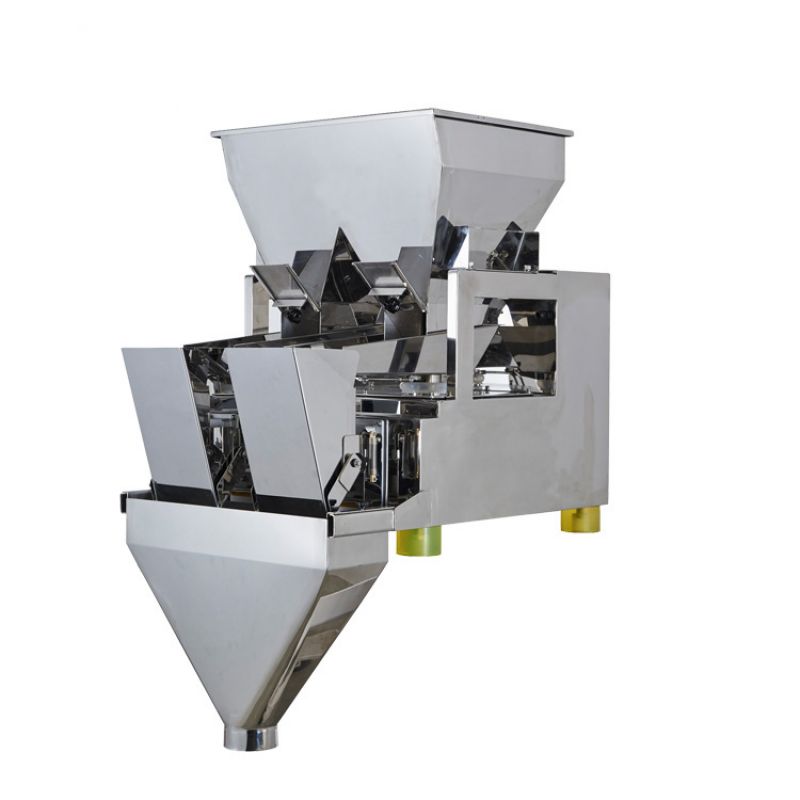
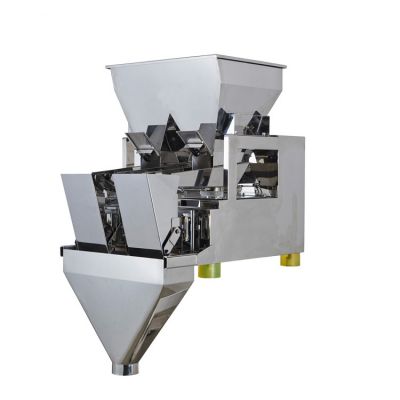
A linear weigher, also known as a linear weighing machine or linear weighing scale, is a specialized piece of equipment used in the packaging industry to precisely measure and dispense a predetermined quantity of loose, granular, or small piece products, such as grains, nuts, snacks, candies, and other similar items. Linear weighers are commonly found in food processing plants, pharmaceutical companies, and various other industries where accurate product portioning is essential. Here's how a linear weigher typically works:
-
Hopper or Feeding System: The process begins with a hopper or feeding system that stores and supplies the bulk product to be weighed. The product is often poured into a vibratory feeder or a bucket conveyor that transports it to the next stage.
-
Feeding Mechanism: The product moves along the linear weigher on a conveyor belt or vibrating trough. Multiple vibrating pans or buckets are arranged in a linear fashion.
-
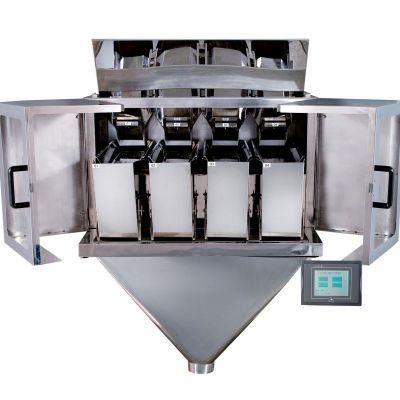
Weighing Buckets or Pans: Along the linear path, there are individual weighing buckets or pans, each of which can hold a specific amount of the product. The number of buckets or pans can vary depending on the design and capacity of the linear weigher.
-
Load Cells or Sensors: Each weighing bucket is equipped with load cells or sensors that measure the weight of the product within the bucket. These load cells provide continuous feedback to the control system.
-
Control System: The control system of the linear weigher monitors the weight measurements from the load cells and calculates the total weight of the product in the buckets. It compares this weight to the target weight or portion size programmed into the machine.
-
Adjustment and Dispensing: The control system can adjust the speed of the conveyor and the duration that the buckets remain open to ensure that the correct amount of product is dispensed into each container or packaging unit.
-
Discharge Chute: After the product is accurately measured and portioned, it is released from the weighing buckets through discharge chutes or funnels, falling into packaging containers such as bags, boxes, or containers on a production line.
-
Feedback and Fine Tuning: Linear weighers often have feedback mechanisms to make fine adjustments and ensure consistent accuracy over time. If variations occur, the control system can adjust the parameters to maintain precision.
The key advantages of linear weighers include their speed, accuracy, and versatility. They can handle a wide range of product types and sizes, making them suitable for many applications in the packaging industry. Linear weighers are commonly integrated into automatic packaging lines, helping companies optimize their production processes and reduce product giveaway or waste
Select a Linear Weigher Solution